https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2024/mar/20/nuclear-plant-closure-carbon-emissions-new-york
When New York’s deteriorating and unloved Indian Point nuclear plant finally shuttered in 2021, its demise was met with delight from environmentalists who had long demanded it be scrapped.
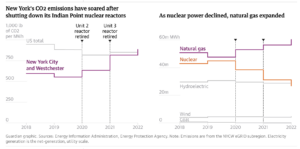
But there has been a sting in the tail – since the closure, New York’s greenhouse gas emissions have gone up.
Castigated for its impact upon the surrounding environment and feared for its potential to unleash disaster close to the heart of New York City, Indian Point nevertheless supplied a large chunk of the state’s carbon-free electricity.
Since the plant’s closure, it has been gas, rather then clean energy such as solar and wind, that has filled the void, leaving New York City in the embarrassing situation of seeing its planet-heating emissions jump in recent years to the point its power grid is now dirtier than Texas’s, as well as the US average.
“From a climate change point of view it’s been a real step backwards and made it harder for New York City to decarbonize its electricity supply than it could’ve been,” said Ben Furnas, a climate and energy policy expert at Cornell University. “This has been a cautionary tale that has left New York in a really challenging spot.”
The closure of Indian Point raises sticky questions for the green movement and states such as New York that are looking to slash carbon pollution. Should long-held concerns about nuclear be shelved due to the overriding challenge of the climate crisis? If so, what should be done about the US’s fleet of ageing nuclear plants?
For those who spent decades fighting Indian Point, the power plant had few redeeming qualities even in an era of escalating global heating. Perched on the banks of the Hudson River about 25 miles north of Manhattan, the hulking facility started operation in the 1960s and its three reactors at one point contributed about a quarter of New York City’s power.