Climate Depot Special Report
https://www.cnn.com/2023/02/07/health/superbugs-climate-change-scn/index.html
“As we get a more extreme climate, especially as it warms, the gradients that drive the evolution of resistance will actually accelerate. So, by curbing temperature rises and reducing the extremity of events, we can actually then fundamentally curb the probability of evolving new resistance,” Dr. David Graham, a professor of ecosystems engineering at Newcastle University and one of the UN report’s authors, said at a news conference ahead of the report’s release.
Experts also say severe flooding as a result of climate change can lead to conditions of overcrowding, poor sanitation and increased pollution, which are known to increase infection rates and antimicrobial resistance as human waste, heavy metals and other pollutants in water create favorable conditions for bugs to develop resistance.
“The same drivers that cause environmental degradation are worsening the antimicrobial resistance problem. The impacts of antimicrobial resistance could destroy our health and food systems,” Inger Andersen, the UN Environment Programme’s executive director, said at the news conference.
…
“Climate change, pollution, changes in our weather patterns, more rainfall, more closely packed, dense cities and urban areas – all of this facilitates the spread of antibiotic resistance. And I am certain that this is only going to go up with time unless we take relatively drastic measures to curb this,” said Dr. Scott Roberts, an infectious diseases specialist at Yale School of Medicine, who was not involved with the new UN report.
#
Full UN Report: “Bracing for Superbugs: Strengthening environmental action in the One Health response to antimicrobial resistance” – Released February 7, 2023
file:///Users/marcmorano/Downloads/antimicrobial_Report.pdf
The report Bracing for Superbugs: Strengthening environmental action in the One Health response to antimicrobial resistance provides evidence that the environment plays a key role in the development, transmission and spread of AMR.
Excerpts: AMR challenges cannot be understood or addressed separately from the triple planetary crisis of climate change, biodiversity loss and pollution and waste because they are all driven by unsustainable consumption and production patterns (Cavicchioli et al. 2019; UN 2022).
…
The climate crisis has numerous impacts on ecosystems, human health, animal health and food production, which also affect AMR (Global Leaders Group [GLG] on AMR 2021a). Higher temperatures can be associated with increased frequency of horizontal gene transfer, especially those associated with conjugation (Lerman and Tolmach 1957; Kim, Kim and Kathariou 2008; Vegge et al. 2012), as well as an increase in antimicrobial resistant infections (MacFadden et al. 2018; McGough et al. 2020; Pepi and Focardi 2021). The climate crisis also contributes to the emergence and spread of AMR in the environment due to the continuing disruption of the environment due to extreme weather patterns (Burnham 2021). Additionally, the frequency, composition and amounts of pollution containing biotic and abiotic agents may be increasing due to the climate crisis. Temperature, oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations in the environment can also influence the survival and proliferation of bacteria, and the rate at which they acquire resistance (Liao, Chen and Huang 2019; Gupta, Laskar and Kadouri 2016; Jong et al. 2020).
…
Moreover, disruption of soil and changing weather and climate may affect valley fever (coccidioidomycosis), caused by Coccidioides, and these infections, as well as those from Candida auris, have been documented as severe and multi-drug resistant (Toda et al. 2019; US CDC 2019).
…
Global governance is increasingly recognizing environmental dimensions of AMR. Calls have been made to address environmental considerations and to include them in global, regional and national governance for a ‘One Health’ response to AMR.
…
Thus, countries need to integrate such environmental considerations into AMR National Action Plans, and AMR into environmental-related plans such as national chemical pollution and waste management programmes, national biodiversity and climate change planning.
#
 .
. 

 .
.
“Climate change is creating a new age of infectious dangers.”Climate Change Could Spark Future Pandemics – “The research, published in Nature, uses modeling to map how climate change could shift the geographic ranges of 3,100 mammals species and the viruses they carry by 2070. … The findings suggest that climate change could “easily become the dominant [human] driver” of cross-species virus transmission by 2070, the authors say.”
#
Marc Morano: “They want to keep both climate and COVID fears humming along to push their so-called solutions, so what better way than to merge the two issues!? Worried about COVID-19, then support the UN Paris climate pact, the Green New Deal, carbon taxes, etc. or else you are a gramma killer!”
#
Restrict anesthesia to save climate & Harvard Med to ‘Integrate Climate’ Into M.D. Curriculum & American Cancer Society Frets ‘carbon footprint of cancer care’ – The Great Medical Reset: Your Doctor will treat the climate first — not your well-being — and you will be happy. Doctors care more about planetary care than patient care.
#
Claim: Deadly fungal infection ‘Valley Fever’ is spreading across USA ‘because of climate change’ – Researchers predict that by 2100, US case numbers will increase by 50 percent – Spread is due to global warming, meaning more hot areas for the fungus to grow. … The fungus is endemic to the desert-like parts of the Southwest, and 97 percent of all American cases are found in Arizona and California. But a study in the journal GeoHealth predicted that, due to climate change, the endemic region of the fungus will spread north to include dry western states such as Idaho, Wyoming, Montana, Nebraska, South Dakota, and North Dakota. In a high-warming scenario, this would mean that by 2100 the number of affected states could rise from 12 to 17, while the number of cases could increase by 50 percent.
Gore’s new health warning: ‘Every organ system can be affected by climate change’
CNN: Further corruption of public health orgs: More than 230 medical journals warn (made-up number of) 1.5°C of ‘global warming’ could be ‘catastrophic’ for health – (Despite 99% drop in climate-related deaths since 1920!) – Human health is already being harmed by the climate crisis, and the impacts could become catastrophic and irreversible unless governments do much more to address global warming, the editors of more than 230 medical journals said in a joint editorial Monday..Among them are an increase in heat deaths, dehydration and kidney function loss, skin cancer, tropical infections, mental health issues, pregnancy complications, allergies, and heart and lung disease, and deaths associated with them…”Despite the world’s necessary preoccupation with Covid-19, we cannot wait for the pandemic to pass to rapidly reduce emissions,” the authors wrote, calling on governments to respond to the climate crisis with the same spirit of “unprecedented funding” dedicated to the pandemic.
#
Reality Checks:
The Collapse of Climate-Related Deaths: Deaths have ‘fallen over 90% since 1920’
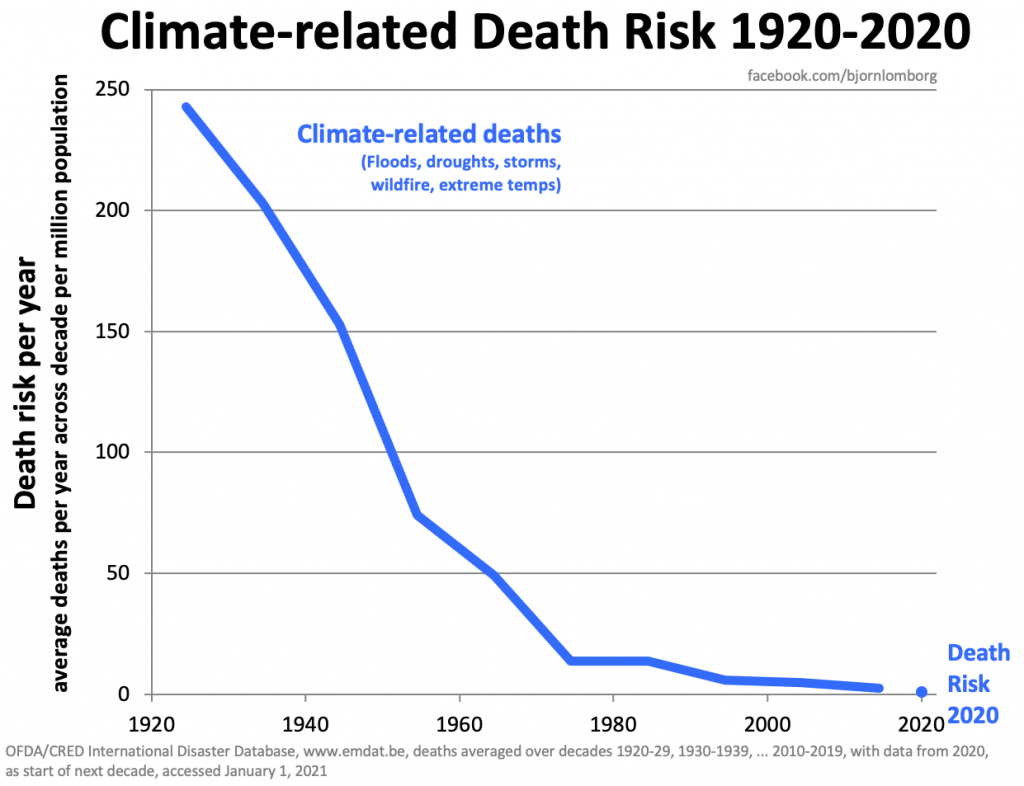
Global Warming Is Actually Sparing Lives …Cold Kills 17 Times More Than Heat, According To Lancet!
Cold kills 20 times more people than Heat
 .
.
Rutgers University – Aug 5, 2020:“The changes in the environment and biodiversity brought on by climate change could be responsible for increases in allergies, autoimmune diseases and autism, according to a Rutgers researcher. Climate change and disruption of the ecosystem have the potential to profoundly impact the human body. Xue Ming, professor of neurology at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, who recently published a paper in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health on the effects of climate change on allergies, autoimmunity and the microbiome — the beneficial microorganisms that live on and inside the human body — discusses how the delicate balance of the environment affects conditions such as allergies, autism and immune disorders.”
Rutgers Neurology Prof. Xue Ming: “We must end the destruction of our natural environment, decrease emissions of greenhouse gases and adopt more “green” behavior. With research demonstrating links between the microbiome and autoimmune, inflammatory and neurologic diseases, it is critical that we minimize antimicrobial exposure.”
Could disturbances in gut bacteria affect the autism rate? Prof. Xue Ming: “The loss of biodiversity related to climate change may affect the microbiome, potentially leading to inflammatory, autoimmune and neurologic diseases. Immunologic disorders, such as food allergies, are on the rise. For example, several studies have found that increases in carbon dioxide and temperature are correlated with changes in the composition of the peanut, making it more difficult for the body to adapt immunity.”
Flashback 2014: Heinz funded study: ‘Autism Linked to Man-Made Climate Change’