https://rclutz.wordpress.com/2020/07/20/cal-carbon-market-fails-in-practice-and-in-theory/
Severin Borenstein explains at energypost.euCalifornia learns even flexible Emissions Markets won’t guarantee price stability. Despite the author’s belief in reducing CO2 emissions, cap and trade is failing to deliver. Excerpts in italics with my bolds.
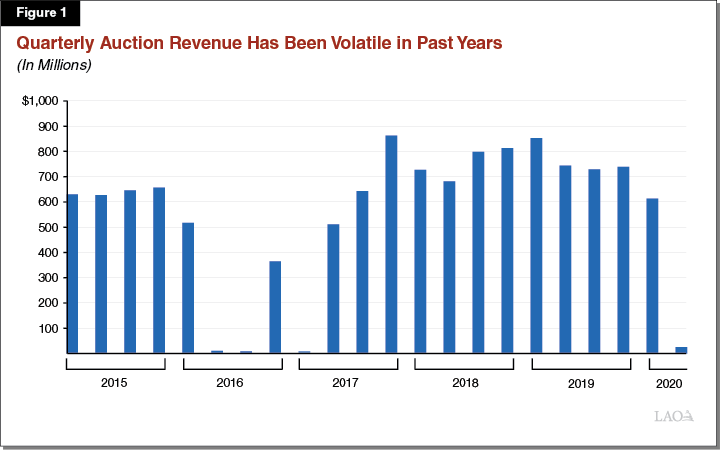
After California’s May allowance auction settled at the minimum price and generated almost no revenues for the state, the long knives are again out in Sacramento for the state’s cap and trade program. What’s the point of a carbon market, some are asking, if price and revenue volatility make planning nearly impossible?
The disappointing auction has caused proposals for stabilising the market price – such as those from the Independent Emissions Market Advisory Committee (IEMAC) in its 2019 report – to be taken more seriously, as they should be. But the tweaks suggested by the IEMAC and others aren’t likely to live up to the expectations of policymakers. That’s not because the proposed changes are unwise, but because the policymakers’ expectations are unrealistic.
Many California regulators and legislators want cap and trade to guarantee that the state reaches prescribed emissions targets by 2030, while at the same time maintaining a moderate allowance price, not at the floor, but not too high. Only by a stroke of pure luck could the program deliver on both. To see why, let’s revisit the design options for an emissions market.
Carbon prices can rise too high or fall too low
Cap and trade “classic” simply sets a cap on emissions and lets the price do all the work to get us there, with no restrictions. But if the demand for emitting the pollutant is high – which could be driven by a strong economy, cheap fossil fuels, and/or slow progress in low-emissions technologies – the price could spiral to astonishing levels. Cap and trade classic generally would get you to the emissions quantity, but possibly at an unacceptable economic or political cost.
And if the demand for emitting is low – such as results from an economic downturn, expensive fossil fuels, and/or competitive low-carbon alternatives – it is quite possible to end up with a price of zero and no further incentive to ratchet down emissions at all.
The price in cap and trade classic is hard to predict, because the future of the economy, fossil fuels, and emissions reduction technologies are hard to predict.
Emissions taxes: a fixed disincentive has its limitations too
Emissions tax “classic” does the opposite. It sets a fixed price, which establishes a constant incentive to reduce pollution regardless of how much is being emitted. But then polluters emit whatever quantity they choose as long as they are willing to pay the tax. If the demand for emitting is high, the outcome will be high levels of emissions.
In economic parlance, where cap and trade classic creates a vertical supply curve for emissions allowances (at a fixed quantity) and emissions tax classic creates a horizontal supply curve for allowances (at a fixed price), the new and improved cap and trade creates an upward sloping supply curve for allowances, restricting the quantity somewhat when demand and price are low, which prevents the price from going even lower, and expanding the quantity somewhat when they are high, preventing the price from going even higher.
What these modifications do is share the impact of unpredictable emissions demand between quantity adjustment and price adjustment, rather than putting the impact of demand uncertainty all on quantity (emissions tax classic) or all on price (cap and trade classic). What they don’t do is get us to the policymakers’ nirvana of predictable emissions quantity and price. Until someone figures out how to reliably predict both macroeconomic growth and technological progress that won’t be a realistic goal.
That’s not a flaw in emissions pricing. It’s a reality of any type of emissions control policies. Technology mandates – the alternatives to pricing – generally don’t ensure a total level of emissions (usually just emissions intensity), and never ensure the cost of achieving a given level of emissions.
A market based on the non-delivery of a non-good, What could go wrong? Let us count the ways
Background from Previous Post

Context: As the image shows, alarmist/activists understand Climate Change (man made assumed) as a concept that depends on three assertions being true. The first one is the science bit, being the unproven claim that humans make the planet warmer by burning fossil fuels. (See Global Warming Theory and the Tests It Fails) The second one is the claim from billions of dollars invested into researching any and all negative effects from global warming, from Acne to Zika virus. The third and also necessary leg is the assertion that governments can act to prevent future warming.
From time to time it is instructive to hear from those who buy into the first two, but have lost confidence in the policies proposed as remedies. Jeffrey Ball writes at Science Direct, not questioning climate science or feared impacts, but distraught about the failed efforts to do something to reduce emissions. His article is Hot Air Won’t Fly: The New Climate Consensus That Carbon Pricing Isn’t Cutting It Excerpts in italics with my bolds.
Jeffrey Ball, a writer whose work focuses on energy and the environment, is the scholar-in-residence at Stanford University’s Steyer-Taylor Center for Energy Policy and Finance and a lecturer at Stanford Law School. He also is a nonresident senior fellow at the Brookings Institution. His writing has appeared in Foreign Affairs, Fortune, Mother Jones, The Atlantic, New Republic, The New York Times, and The Wall Street Journal, among other publications. Ball, previously The Wall Street Journal’s environment editor, focuses his Stanford research on improving the effectiveness of clean-energy investment, particularly in China.
Carbon Pricing Isn’t Cutting It
In the history of climate change, 2018 will go down as a year when certain facts finally hit home, truths inconvenient for partisans on all sides. Those on the right, at least those who have been arguing that greenhouse-gas emissions aren’t a significant problem, wereforced to recognize that those emissions are causing real harm to real people right now.Those on the left, at least those who have put their faith in the promise of renewable energy to cool the planet, had to reckon with the reality that, even as those technologies boomed,carbon emissions continued to grow. And those across the political spectrum who had been calling for what seemed in theory a sensible climate policy—putting a price on carbon emissions—had to concede that theirsupposed solution isn’t helping much at all.
(My comment: Like so many true believers, Ball casts climate change as a political issue between left and right wings. Note he does think we can all agree that policies are not working.)
No single event can be attributed to climate change, but scientists cite a lengthening list of unfolding events, from wildfires in California to drought in Europe to rising waters along Bangladesh, as evidence of the effects of a warming world. Even the administration of US President Donald Trump, which has rolled back myriad climate policies, noted in a November report, the latest legally mandated US National Climate Assessment, that the effects of climate change “are already being felt in communities across the country”—from intensifying flooding in the nation’s northeast region, to worsening drought in the southwestern part of the country, to rising temperatures and erosion that are damaging buildings in Alaska.
(My comment: Ball does not acknowledge rebuttals and challenges to the recent NCA document that merely repeated claims from previous editions, and echoed the feverish exhortations from IPCC SR15. But this paragraph was aimed at the skeptical on the right, while soothing the believers on the left. Let’s now get into the meat of it: Is the government stopping it?)
Renewable energy isn’t stopping that. It represented 70% of net new power-generating capacity installed globally in 2017, a stunning share that reflects falling costs and rising penetration. Yet for all that growth, renewable energy still provided only an estimated 14% of total global energy in 2017, up about 1 percentage point from its share in 2000, because fossil-fuel energy capacity also has been increasing. Indeed, even as renewable-energy capacity hit an all-time high, energy-related carbon emissions did too. They rose 1.6% in 2017, following three years in which they were flat, and they are expected to have risen further in 2018.
Emissions are increasing even though more governments than ever before have imposed prices on carbon emissions, either levying a carbon tax or instituting a cap-and-trade system of pollution permits so that those who emit greenhouse gases have a financial incentive to reduce them. That is little wonder, given that less than 1% of global carbon emissions are subject to a price that economists peg as high enough to meaningfully curb them.
This past June, in an essay in Foreign Affairs, “Why Carbon Pricing Isn’t Working,” I cataloged evidence that carbon pricing is failing to meaningfully reduce carbon emissions around the world—from Europe, where the policy took significant hold, to California, where leading policymakers have embraced it, to China, which is in the early stages of ramping up what will be by far the biggest carbon-pricing regime on the planet. I argued that, though in theory carbon pricing makes sense, in practice it is failing, for two reasons: structurally, carbon pricing tends toconstrain emissions mostly in the electricity sector, leaving the transportation and building sectors largely unaffected; and politically, even those governments that have imposed carbon prices have lacked the fortitude to set them high enough to significantly curb even electricity emissions. As a result, I wrote, “a policy prescription widely billed as a panacea is acting as a narcotic. It’s giving politicians and the public the warm feeling that they’re fighting climate change even as the problem continues to grow.” Not just ineffective, carbon pricing is proving counterproductive, because “it is reducing the pressure to adopt other carbon-cutting measures, ones that would hit certain sectors harder and that would produce faster reductions.” Among those other needed measures: phasing out coal as a power source except where it is burned with carbon-capture- and -sequestration technology, which minimizes its emissions; maintaining, rather than closing, nuclear plants; makingrenewable energy cheaper; and mandating greater energy efficiency.
Would that the half year since that essay was published had proven its assessment too harsh. Unfortunately, recent events and analyses have only bolstered it. Since the summer, and in the lead-up to the latest global climate-policy conference, this month in Poland, studies exploring carbon pricing’s shortcomings have begun piling up. They now amount to a new and sobering climate-literature genre.
Belief in carbon pricing was strong in 2015, when policymakers from some 190 countries issued the Paris Agreement, calling for measures to keep the increase in the average global temperature “well below” 2°C above preindustrial levels and for “pursuing efforts” to keep the rise below 1.5°C.6 Unlike prior climate agreements, notably the Kyoto Protocol, which nearly two decades earlier had pressed for emission cuts only from developed countries, the Paris Agreement included specific emission-reduction pledges even by China, India, and other developing countries, which now produce the bulk of global emissions. But the pledges countries made in Paris werevoluntary rather than mandatory, and most were relatively weak. Even if countries made good on them, it was clear, the world would not cut emissions anywhere near enough to avoid crashing through the 2°C threshold.
Coming out of Paris, carbon pricing was a presumption. In 2017, a group of leading economists backed by the World Bank and called the High-Level Commission on Carbon Prices announced that meeting the Paris temperature targets would require carbon prices of US$40 to $80 per metric ton of carbon dioxide by 2020 and of $50 to $100 per ton by 2030. But in May the World Bank reported that, though the percentage of global greenhouse-gas emissions subject to carbon prices had risen to 20%, only 3% of those emissions were priced at or above the important $40 level. In other words, fewer than 1% of all global greenhouse-gas emissions are priced at a level likely to constrain them.
Carbon-pricing regimes are spreading, and some are being toughened, but neither is happening quickly enough to make much environmental difference. The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), parsing the numbers somewhat differently than does the World Bank, calculates that 76.5% all energy-related carbon dioxide emissions in OECD and Group of 20 (G20) countries either aren’t priced at all or are priced below 30 euros per metric ton of carbon dioxide, a level the OECD calls “a low-end estimate of the damage that carbon emissions currently cause.” That “carbon gap,” in OECD parlance, has narrowed by just 1 percentage point in each of the past three years—hardly a relevant climate win.
It is against this backdrop that critiques of carbon pricing have begun to accumulate. One of the more notable was published in August by the International Monetary Fund (IMF), whose head, Christine Lagarde, has been an enthusiastic supporter of carbon pricing. She called in 2017 for this response to carbon dioxide: “Price it right, tax it smart, do it now.” As the IMF’s new working paper makes clear, most carbon prices thus far imposed haven’t been right, relying on carbon taxes hasn’t been terribly smart, and, if “it” means a serious response to climate change, the world isn’t doing it now.
The authors of the IMF study used a model to project how carbon prices at two levels by 2030—$35 per metric ton of carbon dioxide and $70 per ton—would affect emissions in the G20 economies. (Few countries have imposed a carbon price anywhere near even the lower of those numbers.) The IMF model clarifies why the world’s largest economies find it so economically and politically difficult to impose a robust price on carbon, just how inadequate were the pledges most countries made in Paris, and how wrenching it will likely be even for countries that made relatively significant Paris pledges to follow through on those promises.
Carbon pricing, as I noted in Foreign Affairs in June, “works well for industries that use a lot of fossil energy, that have technologies available to them to reduce that energy use, and that can’t easily relocate to places where energy is cheaper.” That is why it tends to bite first in the electricity sector. The IMF model underscores this, concluding that the major determinant of how significantly a givencarbon price will curb emissions in a given country is the extent to which that country’s electricity sector relies on coal. A $70 carbon tax, the IMF model projects, would cut emissions by significantly more than 30% in coal-dependent China, India, and South Africa; by some 15%–25% in such countries as the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom; and by less than 15% in coal-light France and Saudi Arabia.9 (That helps explain why, among all these countries, only France has imposed a carbon price above $40 per ton. Andeven France has difficulty raising the effective price on carbon, as the recent Yellow Vest protests, which led France to suspend a proposed fuel-tax increase, show.)
That carbon pricing hits hardest in coal-reliant places helps explain its political difficulties. The IMF’s modeled carbon tax is particularly regressive—meaning its cost falls particularly heavily on the poorest—in China and the United States, the world’s two top carbon emitters. (Electricity access in these two coal-heavy nations is broad, meaning the poor there tend to spend a greater portion of their income on carbon-intense power than do the rich.) Although both countries are experimenting with carbon pricing, it is little surprise that the prices in both remain low. In California, carbon prices are higher than in other parts of the United States that have implemented them, but California gets only a small amount of its electricity from coal—and most of that is imported from other states—which bolsters the point. The IMF analysis also helps clarify why China, the world’s top coal burner, proffered a relatively weak Paris pledge. Some governments are trying to counteract the regressive nature of carbon pricing by layering on structures to return all or some of the resulting revenue to consumers—a worthwhile idea. But even those structures have faced opposition in coal-reliant jurisdictions.
Even some countries whose Paris pledges were more robust are likely to have difficulty following through on them. Those pledges “might imply increases in energy prices (and burdens on vulnerable groups) that push the bounds of political acceptability,” the IMF paper notes. A meaningful reduction in carbon emissions, the IMF concludes, would require backstopping countries’ Paris pledges in two ways: by imposing carbon-price floors—levels below which countries decree that their carbon prices will not fall—and by imposing policies other than carbon pricing that force deeper cuts. Inoffensive carbon pricing alone won’t cut it.
Even extraordinarily high carbon prices are failing in important ways to spur significant carbon cuts. A piece published in Energy Policy in late June by Endre Tvinnereim and Michael Mehling explores the uninspiring example of Sweden. The small Scandinavian country has, according to the World Bank, the highest carbon price in the world, at $126 per ton, based on current currency-exchange rates.4 Yet in the quarter century between 1990, when Sweden introduced its carbon tax, and 2015,carbon emissions from Swedish road transportation fell only 4%. Meanwhile, sales in Sweden of new internal-combustion vehicles continue to rise, imposing what the authors call “carbon lock-in” from vehicles likely to remain on the road a decade or more.What’s needed, they argue, are bans on the sale of new internal-combustion cars, bans of the sort that have been proposed in such countries as China, India, France, the United Kingdom, and Norway. Pricing carbon “is useful,” they write, “but far from sufficient to achieve deep decarbonization.”
The authors are right that policies beyond carbon pricing are needed. But clarity about the goal of such policies is key. Some recent critiques of carbon pricing, at least implicitly, construe success in fighting climate change as requiring the near-total replacement of fossil fuels with renewable energy. Plenty of evidence, however, suggests that structuring the climate fight primarily as a pursuit of renewables is neither realistic nor particularly smart.
The goal in fighting climate change is not to end the use of fossil fuels. The goal is to fuel the world while cutting carbon emissions essentially to zero. That will require dramatically lowering the cost and thus boosting the penetration of renewable and other non-fossil energy sources. It also will mean ensuring that the large quantities offossil fuels that are all but certain to continue to be burned for decades to come are burned using technologies that slash the amount of carbon dioxide their combustion coughs into the atmosphere.
The policies necessary to achieve these twin ends will be complex. A meaningful carbon price would help them, but in most of the world there is little evidence policymakers have the stomach to impose one. Climate change is real. Fighting it demands—from everyone involved—more than rhetoric. That this message is getting across is a good sign.
My Concluding Comment

The graph illustrates the problem very clearly. Since 1994 there have been 24 Conferences of the Parties (COP), along with numerous other meetings. These UNFCCC discussions have utterly failed to reduce CO2 emissions. Yet from 2020, emissions have to drop dramatically, if we are to stand a chance of keeping global warming below 1.5°C.
According to IPCC SR15 this will require an annual average investment of around US$2.4 trillion (at 2010 prices) between 2016 and 2035, representing approximately 2.5% of global gross domestic product (GDP). The cost of inaction and delay, however, will be many times greater. (sic). Note: This is referring to increasing investments in renewable energy from current US$335B per year to $2.4T. Present global spending on Climate Crisis Inc. is estimated at nearly US$2T, not limited to renewables. So this would double the money wasted spent on this hypothetical problem.

After reading Ball’s assessment it is obvious that carbon pricing will only reduce emissions by crashing national economies. The fear of CO2 leads directly to discussion of stopping modern societies in their tracks. Talking about policies that “bite” this or that sector equates to intentionally dictating economic decline, industry by industry. And Ball suggests that ever more intrusive bans and regulations must be added on top of higher carbon prices in order to save the planet from our way of life.
This analysis has been preceded by numerous doomsday deadlines over the decades which we have passed and not suffered in the least. Can we finally dismiss the illusion that we humans control the temperature of the planet? Can we stop the crazy schemes to cut our CO2 emissions, and appreciate instead the greening of the biosphere?
Rational public policymakers can not presume the climate will be unchanging in the future. Our experience teaches that there will be future periods both warmer and cooler than the present. History also shows that cold periods are the greater threat to human health and prosperity. Instead of wasting time and resources trying to control the future weather, we should be preparing to adapt to whatever nature brings. The priorities should be to ensure affordable and reliable energy and robust infrastructure.
See Also IPCC Freakonomics





